Forestry

Basal area is an important unit of measurement in forestry and land management, but it can often be misunderstood, even by professionals. Learn what basal area is, why it is used as a measurement instead of trees-per-acre, and how it is calculated. Included are several diagrams and tables, a glossary, and a list of further resources.
Assume you have 40 acres of forestland that was recently assessed by a natural resource professional. The resulting timber appraisal states that there is an estimated 90 square feet of basal area per acre and the trees have an average diameter of 10 inches. What does that really mean? From the description, can you picture what the forest looks like? Or more importantly, do you know how that number could be used to help you with future forest management options?
From time to time, you might encounter unfamiliar forestry terms as you interact with land management professionals or read forestry- and wildlife-related publications. Indeed, basal area might be one of these unfamiliar terms. For foresters, basal area is one of the most easily understood terms, but it may also be one of the most misused terms in forestry. This publication will help you better understand what basal area is and why it is an important forest measurement.
Basal area is used to determine more than just forest stand density; it is also linked with timber stand volume and growth. Therefore, it is often the basis for making important forest management decisions such as estimating forest regeneration needs and wildlife habitat requirements. The manipulation of stand basal area to achieve forest management goals can be as important as the use of prescribed fire or other vegetation treatments.
What Is Basal Area?
Part of the confusion about the term might have to do with the fact that basal area can be thought of in two different ways:
The basal area of a tree is defined as the cross-sectional area (usually in square feet) of a single tree at breast height, or 4. feet above ground. The diameter of a tree at 4. feet above the ground is called diameter at breast height (DBH).
The cross-sectional area of all stems of a species or all stems in a stand measured at breast height and expressed as per unit of land area.
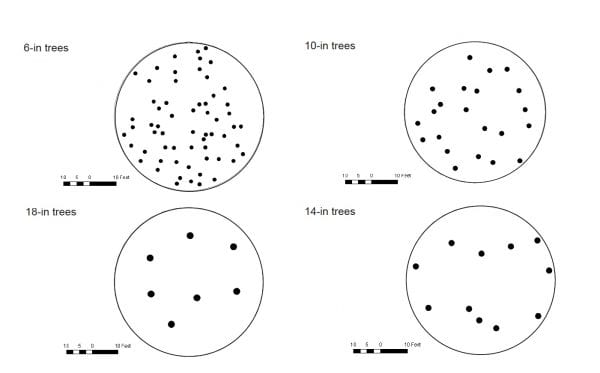
Figure 2. Representation of a 1/5-acre plot and the number of trees at 6, 10, 14, and 18 inches DBH that are needed to make 60 square feet of basal area per acre. (Graphic courtesy John Gilbert, Longleaf Pine Stand Dynamics Lab, School of Forestry and Wildlife Sciences, Auburn University)
Why Not Trees Per Acre?
Trees per acre (TPA) is a common measure of the number of standing trees that are found on an acre of land. It is also relatively easy to understand as a way to calculate stand density, or how crowded trees are in a stand. Trees per acre does not take into account the size of trees; instead it is based on the distance between or the spacing of trees on a site. In a plantation, the number of trees per acre can be estimated given the spacing within a row of trees and the distance between the rows.
Trees per acre is an appropriate term to describe stand density in young stands, whether a plantation or naturally regenerated stand. But as trees grow, this becomes less meaningful, especially when estimating timber volumes.
For instance, a stand of 6-inch DBH trees averaging 100 trees per acre does not contain the same volume of wood as 100 trees per acre of 16-inch DBH trees. Similarly, timber stands can have the same basal area yet look very different on the ground. The diameter of trees at DBH determines how many trees per acre it takes to make a given basal area. Figure 2 illustrates graphically how many 6-, 10-, 14-, and 18-inch trees you would have on a 1/5-acre circular plot to make 60 square feet of basal area per acre:
Table 1. Basal Area Per Tree, in Square Feet, for Trees That Are 1 to 30 Inches DBH
| DBH (inches) | BA/tree (ft2) | DBH(inches) | BA/tree (ft2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 1.227 | 30 | 4.909 |
| 14 | 1.069 | 29 | 4.587 |
| 13 | 0.922 | 28 | 4.276 |
| 12 | 0.785 | 27 | 3.976 |
| 11 | 0.66 | 26 | 3.687 |
| 10 | 0.545 | 25 | 3.409 |
| 9 | 0.442 | 24 | 3.142 |
| 8 | 0.349 | 23 | 2.885 |
| 7 | 0.267 | 22 | 2.64 |
| 6 | 0.196 | 21 | 2.405 |
| 5 | 0.136 | 20 | 2.182 |
| 4 | 0.087 | 19 | 1.969 |
| 3 | 0.049 | 18 | 1.767 |
| 2 | 0.022 | 17 | 1.576 |
| 1 | 0.005 | 16 | 1.396 |
Table 2. Number of trees by 1-inch-diameter classes needed to achieve per acre square feet of basal area. Values are rounded to the nearest whole tree.
| Basal area/acre | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 29 | ||||||||||||||
| 29 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 31 | ||||||||||||||
| 28 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 33 | ||||||||||||||
| 27 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 33 | 35 | ||||||||||||||
| 26 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 35 | 38 | ||||||||||||||
| 25 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 23 | 26 | 29 | 32 | 35 | 38 | 41 | ||||||||||||||
| 24 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 22 | 25 | 29 | 32 | 35 | 38 | 41 | 45 | ||||||||||||||
| 23 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | 17 | 21 | 24 | 28 | 31 | 35 | 38 | 42 | 45 | 49 | ||||||||||||||
| 22 | 4 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 19 | 23 | 27 | 30 | 34 | 38 | 42 | 45 | 49 | 53 | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 29 | 33 | 37 | 42 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 58 | ||||||||||||||
| 20 | 5 | 9 | 14 | 18 | 23 | 28 | 32 | 37 | 41 | 46 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 64 | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 36 | 41 | 46 | 51 | 56 | 61 | 66 | 71 | ||||||||||||||
| 18 | 6 | 11 | 17 | 23 | 28 | 34 | 40 | 45 | 51 | 57 | 62 | 68 | 74 | 79 | ||||||||||||||
| 17 | 6 | 13 | 19 | 25 | 32 | 38 | 44 | 51 | 57 | 63 | 70 | 76 | 82 | 89 | ||||||||||||||
| 16 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 29 | 36 | 43 | 50 | 57 | 64 | 72 | 79 | 86 | 93 | 100 | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | 8 | 16 | 24 | 33 | 41 | 49 | 57 | 65 | 73 | 81 | 90 | 98 | 106 | 114 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 9 | 19 | 28 | 37 | 47 | 56 | 65 | 75 | 84 | 94 | 103 | 112 | 122 | 131 | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | 11 | 22 | 33 | 43 | 54 | 65 | 76 | 87 | 98 | 108 | 119 | 130 | 141 | 152 | ||||||||||||||
| 12 | 13 | 25 | 38 | 51 | 64 | 76 | 89 | 102 | 115 | 127 | 140 | 153 | 166 | 178 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 61 | 76 | 91 | 106 | 121 | 136 | 152 | 167 | 182 | 197 | 212 | ||||||||||||||
| 10 | 18 | 37 | 55 | 73 | 92 | 110 | 128 | 147 | 165 | 183 | 202 | 220 | 238 | 257 | ||||||||||||||
| 9 | 23 | 45 | 68 | 91 | 113 | 136 | 158 | 181 | 204 | 226 | 249 | 272 | 294 | 317 | ||||||||||||||
| 8 | 29 | 57 | 86 | 115 | 143 | 172 | 201 | 229 | 258 | 286 | 315 | 344 | 372 | 401 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 37 | 75 | 112 | 150 | 187 | 225 | 262 | 299 | 337 | 374 | 412 | 449 | 486 | 524 | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 51 | 102 | 153 | 204 | 255 | 306 | 357 | 407 | 458 | 509 | 560 | 611 | 662 | 713 | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | 73 | 147 | 220 | 293 | 367 | 440 | 513 | 587 | 660 | 733 | 807 | 880 | 953 | 1027 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 115 | 229 | 344 | 458 | 573 | 688 | 802 | 917 | 1031 | 1146 | 1261 | 1375 | 1490 | 1604 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | 204 | 407 | 611 | 815 | 1019 | 1222 | 1426 | 1630 | 1834 | 2037 | 2241 | 2445 | 2648 | 2852 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | 458 | 917 | 1375 | 1834 | 2292 | 2750 | 3209 | 3667 | 4125 | 4584 | 5042 | 5501 | 5959 | 6417 | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 1834 | 3667 | 5501 | 7334 | 9168 | 11001 | 12835 | 14668 | 16502 | 18335 | 20169 | 22002 | 23836 | 25669 | ||||||||||||||
| Trees/acre | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DBH (inches) | BA10 | BA20 | BA30 | BA40 | BA50 | BA60 | BA70 | BA80 | BA90 | BA100 | BA110 | BA120 | BA130 | BA140 | ||||||||||||||
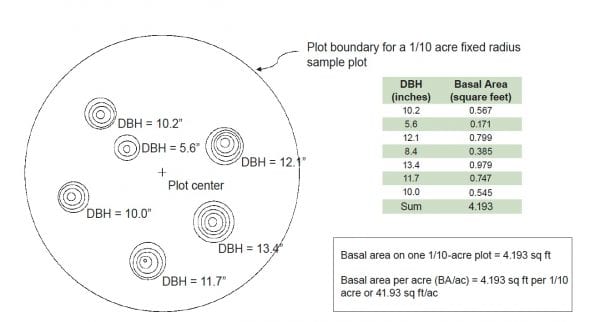
Figure 3. Illustration of how per acre basal area can be calculated for seven trees in a 1/10-acre sample plot. Each stump is labeled with its DBH.
How Is Basal Area Calculated?
Picture an acre of trees cut off at DBH (4. feet). The total surface area of the stumps in square feet would be the basal area of that acre.
In mathematical terms:
Basal area (square feet) = (pi /(4 * 144))*DBH2 = 0.005454*DBH2
Where pi = 3.14, DBH = diameter breast height.
The number 0.005454 is called the foresters constant, which converts the measured inches into square feet.
Based on the calculations above, Table 1 illustrates the square feet of basal area per tree for several DBH classes. Table 2 can serve as a guide to assist landowners and natural resource professionals when estimating trees per acre from certain basal area measurements.
Table 1. Basal Area Per Tree, in Square Feet, for Trees That Are 1 to 30 Inches DBH
| DBH (inches) | BA/tree (ft2) | DBH(inches) | BA/tree (ft2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 1.227 | 30 | 4.909 |
| 14 | 1.069 | 29 | 4.587 |
| 13 | 0.922 | 28 | 4.276 |
| 12 | 0.785 | 27 | 3.976 |
| 11 | 0.66 | 26 | 3.687 |
| 10 | 0.545 | 25 | 3.409 |
| 9 | 0.442 | 24 | 3.142 |
| 8 | 0.349 | 23 | 2.885 |
| 7 | 0.267 | 22 | 2.64 |
| 6 | 0.196 | 21 | 2.405 |
| 5 | 0.136 | 20 | 2.182 |
| 4 | 0.087 | 19 | 1.969 |
| 3 | 0.049 | 18 | 1.767 |
| 2 | 0.022 | 17 | 1.576 |
| 1 | 0.005 | 16 | 1.396 |
How Do I Determine the Basal Area of My Forest Stand?
Basal area per acre can be determined by simply measuring DBH of each tree on the acre, computing each tree’s basal area, then adding each tree’s basal area. Typically, a forested stand is cruised where a subsample of the total area is measured. The results of the subsample measurement is expanded or converted to a per-acre basis.
Another way that foresters may determine basal area is through the use of prisms or angle gauges to estimate basal area. Timber cruises of larger, sawtimber-sized pine stands and bottomland hardwood stands are often completed using this method. A prism or angle gauge is used to determine which trees are in (counted) or out (not counted). In the South, a 10-factor gauge or prism is most commonly used. With a 10-factor gauge or prism, the number of “in” trees is multiplied by 10 to get the basal area per acre. The average of measurements taken at several locations on a stand is used to estimate basal area.
If you do not have a prism or angle gauge, the following is a low-cost alternative.
Using a Penny and a Piece of String to Estimate Basal Area
An angle gauge of sorts can be made with a penny and a piece of string. Angles gauges and 10-factor prisms generate an angle of 1 inch in 33 inches. That is, a 1-inch DBH tree would have to be 33 inches or closer to be “in”; a 2-inch DBH tree would have to be 66 inches or closer to be in, and so on.
The diameter of a penny is 0.75 inches, so if it is held 24.75 inches from your eye, you have a 10-factor angle gauge.
Tie a knot in the end of a piece of string. Measure out 24.75 inches from the knot, and tie another knot. Hold one knot against your cheekbone or in your teeth, and hold the other knot at the penny, extending the penny until the string is taut.
If you want to measure a sample plot, pick a tree to measure first, such as the first tree to the right of due north on a compass heading. Extend the penny out the length of the string over a fixed point on the ground in front of you. If the sides of the tree appear to be beyond the edges of the penny, the tree is in (counted). If the edges of the penny appear to be beyond the sides of the tree, the tree is out (not counted). If the edges and sides appear to be even, count every other tree. See Figures 4 and 5.
Rotate around clockwise, holding the penny as you look at all trees in that area. Count all the “in” trees at that point, multiply by 10, and you have the basal area represented on that plot. To estimate basal area on your site, take the average of several points to gain a more accurate estimate.
How Can an Understanding of Basal Area Help Me More Effectively Manage My Forest Land?
An example: Naturally regenerating a mature longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) stand.
There are many benefits to the natural regeneration of your pine stands. There is no cost for seedlings, and no additional labor is needed for planting. Studies have shown that shelterwood cuts are one of the best ways to promote natural regeneration on longleaf pine forests.
It is recommended that small shelterwood harvest areas of 2 to 4 acres be thinned to approximately 30 square feet of basal area, leaving the highest quality seed-bearing trees in the overstory. To accomplish this, careful timber harvest is critical. Usually, it is recommended that remaining trees should be at least 30 years old and 10 inches or greater in DBH. Seed from these remaining overstory trees will regenerate the stand. Once the new stand of young trees is established, the older sawtimber-sized trees can be removed from the overstory through a series of thinnings.
Shelterwood systems can be used to create small, even-aged patches throughout the forest that mimic the natural regeneration process that evolved with the species. Using Table 2 in this publication, you could determine just how many trees of a given DBH you would need to leave to achieve 30 square feet of basal area per acre. For example, if you had a stand that averaged 12 inches DBH, a basal area of 30 could be achieved with approximately thirty-eight 12-inch trees.
Can Understanding Basal Area Help Me Manage for Wildlife, Too?
An example: Managing forested habitats for Northern Bobwhite Quail (Colinus virginianus)
Assume that you have a forest stand and one of your primary objectives is to manage for Northern Bobwhite Quail habitat. The first step in establishing Northern Bobwhite habitat on your property is to understand what the habitat parameters are and then how those standards apply to forest management. Over the last 45 years Northern Bobwhite populations have declined throughout their range. This decline is due in part to the reduction of habitat quality and quantity. Forest management practices, such as timber harvesting and thinning, have been shown to improve forested habitat for Northern Bobwhite by reducing the density of forest stands.
Actual benefits to wildlife vary by species, timber type, and location; however, widely accepted standards for Northern Bobwhite habitat management suggest that a mosaic of forested and open landscapes is needed. Thinning and prescribed fire are key to effectively creating the open pine canopy with grassy understory that is optimum forested habitat for the species. When tree canopies close, sunlight that is needed for grasses and forbs to develop is unable to reach the forest floor. In many cases thinning prescriptions for forest management objectives are still too dense for Northern Bobwhite habitat management.
Current recommendations state that young pine stands (12 to 18 years) should be thinned as early as possible, and sawtimber and pole stands should be thinned to an overall basal area of less than 40 square feet per acre. Using the BA40 column in table 2, you can determine the trees per acre needed on your stand to help achieve your management goals for Northern Bobwhite.
Basal Area Is Indeed a Measure Used for Management
It can represent the size of individual trees and the density of your forest stands, and it can describe wildlife habitat. Assessed either with special instruments, or everyday items, basal area is an important forest measurement. Remember, it is always best to have a qualified professional forester or wildlife biologist evaluate your property for the best evaluation of your forest resources. Becoming familiar with forestry terms and procedures, however, makes you an informed landowner, better able to make decisions regarding your property.
Glossary
basal area
The measurement of the cross-sectional area of tree trunks at 4. feet above the ground and inclusive of the bark. Basal area gives an idea of the stocking of trees in a stand and is usually reported in square feet per acre.
diameter breast height (DBH)
The measurement of the diameter of a tree stem, outside the bark, taken 4. feet above the ground on the uphill side of the tree.
stand density
The direct measure of crowding of trees in a stand; can be measured in terms of trees per acre, basal area, or volume per acre. Measurements of stand density may be used to determine silvicultural prescriptions.
trees per acre
A measure of stand density determined by the spacing between trees. Trees per acre can be used to estimate timber volumes and silvicultural prescriptions.
References
Burger, L. W. “Northern Bobwhite.” In Wildlife of Southern Forests: Habitat and Management, edited by J. G. Dickson, 122–146. Blaine, WA: Hancock House, 2001.
Croker, T. C. Jr., and W. D. Boyer. “Regenerating Longleaf Pine Naturally,” SO-105. Research paper, USDA Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station, 1975.
Glover, G., and B. Barlow. Forestry Field Measurements Manual (unpublished). Auburn, AL: Auburn University, 2009.
Download a PDF Version of Basal Area: A Measure Made for Management, ANR-1371.

