Finance & Career

Reviewing your credit report is the first step you should take to improve your credit score and to detect any signs of identity theft.
When finance is discussed in today’s media, credit scores are generally mentioned while credit reports are not. This increased emphasis on credit scores has many consumers thinking that a credit score is more important than an actual credit report.
A credit score is much different from a credit report. Reviewing your credit report is the first step you should take to improve your credit score and to detect any signs of identity theft.
Credit Report

Figure 1. Credit report. Stock image by scyther5.
A credit report is a file containing information about your credit history. It provides evidence of how you manage your finances as well as evidence for determining your creditworthiness. The three major credit reporting agencies or bureaus in the United States that create and maintain these files are Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. By law, each of these agencies are required to provide you with one free copy of your credit report each year. However, you must request a copy from each agency. Be sure to request a copy from one of the agencies every four months to monitor your credit report throughout the year.
There are four basic sections on a credit report: personal information, inquiries, public records information, and credit history.
- The personal information section consists of information such as your name, address (past & present), date of birth, social security number and employers (past & present).
- The inquiries section provides information on who has requested your credit report. When someone requests your credit report, it is called an inquiry, pull, or hit. The pull can be soft or hard. You must give your permission as well as complete an application for hard pulls. A hard pull reduces your credit score. A soft pull neither requires your permission or an application. When you request your credit report, it is a soft pull. This type of inquiry DOES NOT decrease your credit score.Bunching allows you to submit several credit applications within a 45-day period without having your score reduced several times. If all the applications are relative to the same item, i.e. mortgage, then the submissions are counted as only one submission. For example, when you do comparison shopping for a home mortgage loan, you will have several mortgage companies pulling your credit report. If it is done within a 45-day period, each inquiry/pull will be bunched together and counted as one hard inquiry/pull.
- The public records section provides information about any financial accounts on which legal actions have been taken. Having legal actions such as bankruptcies, tax liens, and civil judgements against you can reduce your credit score.
- The credit history section provides information on the various types of credit you have received and their status. Information, such as whether payment on the accounts are up to date or behind, will be given.
Credit Score
A credit score is NOT the same as a credit report. Information in the credit report is used to calculate a numerical value that is called a FICO (Fair Isaac Corporation) score or a credit score. Although there are a number of credit scores, the majority of lenders use the FICO score for making informed lending decisions. The score helps a lender determine how risky it is to lend money to an individual. For example, the lower the individual’s credit score, the greater the risk or chance of that individual defaulting on a loan. In other words, a credit score helps lenders make knowledgeable decisions about: a) if they should or should not lend the money; b) how much should they lend; and c) what the interest rate should be.
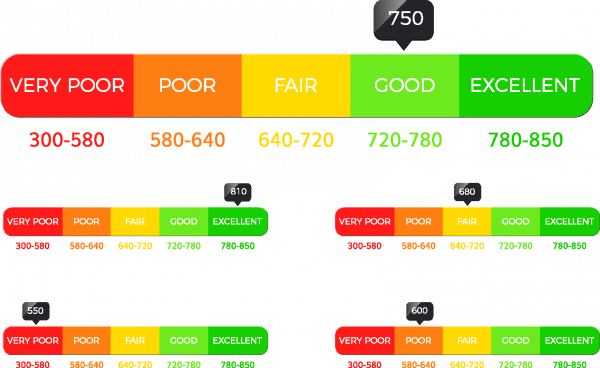
Figure 2. Credit Score Chart. Stock image by Alexey Bezrodny
- 300–580 = Very Poor
- 580–640 = Poor
- 640–720 = Fair
- 720–780 = Good
- 780–850 = Excellent
Just as you have a credit report for each of the three bureaus, you also have a credit score for each credit report. Unlike the credit report that is free, a small fee is usually charged for FICO scores/credit scores. Although credit scores differ slightly, even among the credit bureaus, the credit ratings together with their FICO scores are shown above.
Components of Credit Score
Because your credit score is used in making so many financial decisions, it is important for you to understand the five factors that makes up a credit score. Each component gives the percentage that it contributes to the total credit score. They include length of credit history, credit mix, new credit, payment history, and utilization. As you will note from the table below, 65% of the score is determined by how well you pay your bills and use your credit.
Table 1. Components of Credit Score - LMNOP
| Letter | Explanation | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| L | Length of Credit History
| 15% |
| M | Mix of Credit
| 10% |
| N | New Credit
| 10% |
| O | Owed Amount
| 30% |
| P | Payment History
| 35% |
Summary
The credit score is not the same as the credit report. The credit report contains information about your credit activity. The credit score is a calculation (number) that suggests the likelihood of you repaying money that is borrowed. The credit score is created from the information taken from the credit report. Therefore, the credit score depends on your credit report, and the credit report reflects your understanding of credit and how you manage your finances.
Go to www.annualcreditreport.com to request a free copy of your credit report. You may also contact your local county Extension office if you have questions or concerns regarding a credit report.
References
AnnualCreditReport.com. (2019). All about credit reports. Retrieved from https://www.annualcreditreport.com/whatIsCreditReport.action.
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (2017, August 3). What is the difference between a credit report and a credit score? Retrieved from https:// www.consumerfinance.gov/ask-cfpb/what-is-the-difference-between-a-credit-report-and-a-credit-score-en-2069/.
 Dorothy Brandon, PhD, CPFFE, Consumer Science & Personal Financial Management, Alabama A&M University
Dorothy Brandon, PhD, CPFFE, Consumer Science & Personal Financial Management, Alabama A&M University
New January 2021, Credit Report versus Credit Score, UNP-2165

