Farming

Scouting for insect pests should be regularly and this guide can be used a field scouting guide for basic information. For pest management information, small organic and high tunnel crop producers should use ANR-2190, “Organic Vegetable IPM Slide Chart,” after proper insect identification. Conventional producers should consult the Southeastern Vegetable Production Handbook. Always consult the insecticide label for correct usage.
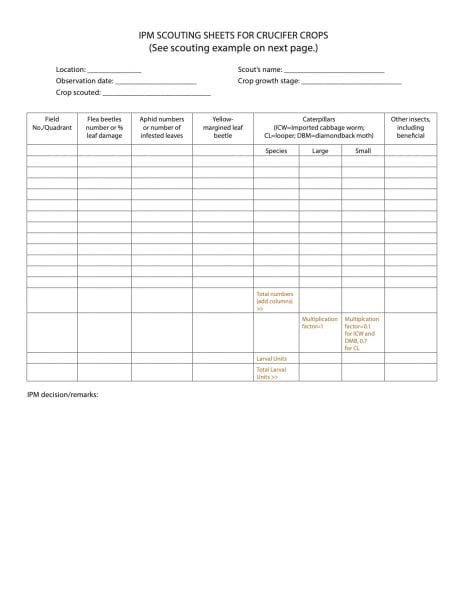
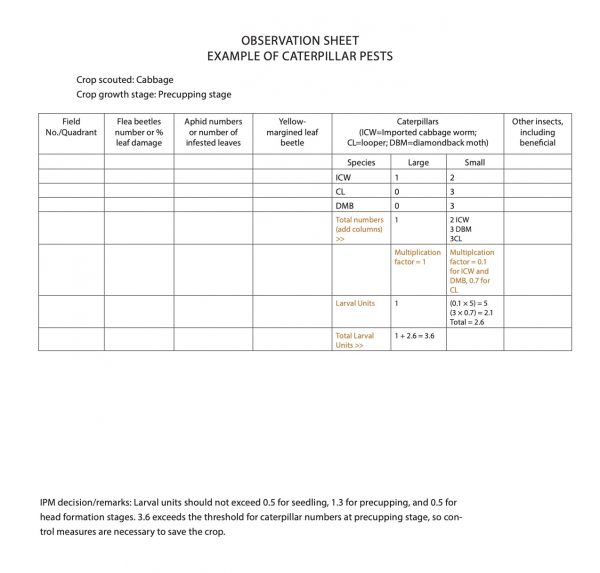
Sampling method: For large acreage, divide the field into four quadrants and scout each quadrant intensively. In a small area, sample 10 locations randomly with four to five plants at each location (sample size of 40 to 50 plants). Count the number of caterpillars separate from aphids or other insects, and refer to the economic thresholds (ET). Use the attached scouting sheet and study the example before scouting. Remember that the accuracy of IPM decision increases with large sample size.
Insect Pest Scouting for Crucifer Crops
ET = Economic threshold (number of insects above which there will be economic losses)
| Name | Identification | Plant Injury | Sampling Method & Economic Threshold (ET) |
|---|---|---|---|
 Beet armyworm (BAW) | Plump green caterpillars up to 30 mm long with three longitudinal stripes on dorsal surface; pair of black spots on the second body segment behind the head | Damaging to young leaves in the fall season; rapid defoliator if uncontrolled in open field and high tunnel crops |
|
 Cabbage aphid | Many species of aphids can be present at one time; soft-bodied insects with winged and wingless forms; winged forms are migratory and may be darker in body color with transparent wings | Large number of aphids can deform plant parts |
|
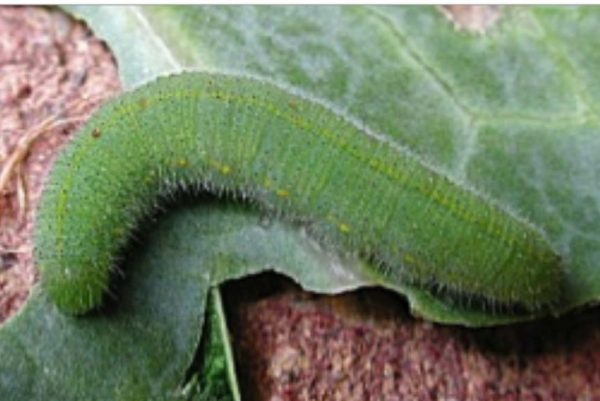 Cabbage butterfly/ Imported cabbageworm (ICW) | Green velvety caterpillars have row of faint yellow spots on each side of body; pupate on undersurface of leaves attached by a silken thread | Velvety caterpillars may feed in groups on old leaves, particularly near leaf veins; caterpillars may move closer to the stalk or near the center head in late stages |
|
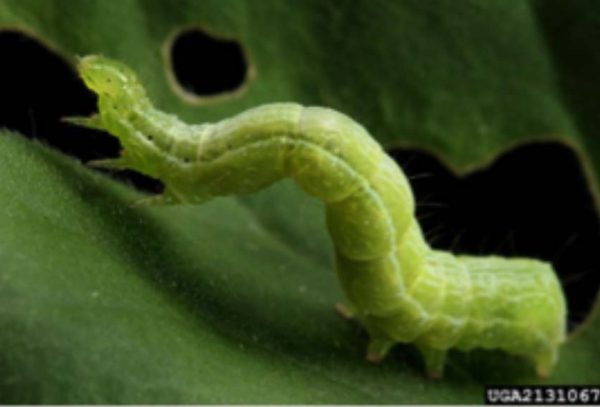 Cabbage looper (CL) | Green caterpillar with several fine longitudinal stripes; head is slightly tapered with broad abdomen; three pairs of green thoracic legs; larvae move in looping fashion | Caterpillars cause leaf skeletonization (everything except the veins are consumed); may occur together with other caterpillars |
|
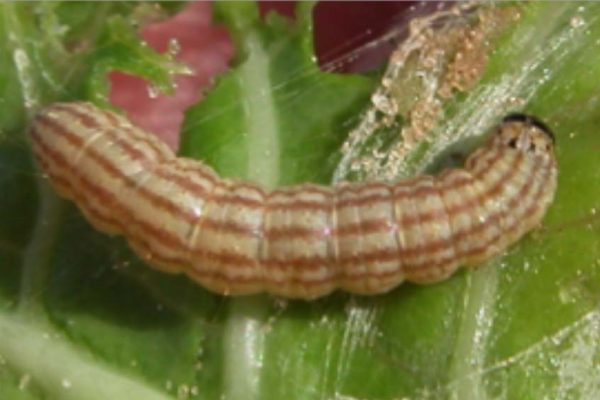 Cabbage webworm (CW) | Yellowish gray caterpillars about 15 mm long; five brown longitudinal stripes on dorsal surface; has distinct body hair | Minor pest in Alabama; larvae cause leaf deformation/webbing; may be found inside webs along the leaf veins (underside) | • Look for webbed leaves. |
 Cross-stripped cabbageworm (C-CW) | Very common in open field and high tunnel crops; late instar caterpillars have grayish blue body with numerous black transverse stripes; stout body hair visible on dorsal surface | Caterpillars feed on buds and tender leaves in masses after hatching, then move out to other leaves; builds up on uncontrolled vegetation |
|
 Diamondback moth (DBM) | Pale green or translucent caterpillars about 7–8 mm long; abdomen is tapered with anal prolegs sticking out (forked appearance); caterpillars wiggle rapidly when disturbed; pupae attached in loose cocoon on leaves; adult moths have diamond-shaped markings on folded wings | Most active in early spring and summer; larvae feed on underside and riddle leaves with holes rapidly; may have resistance to many synthetic insecticides |
|
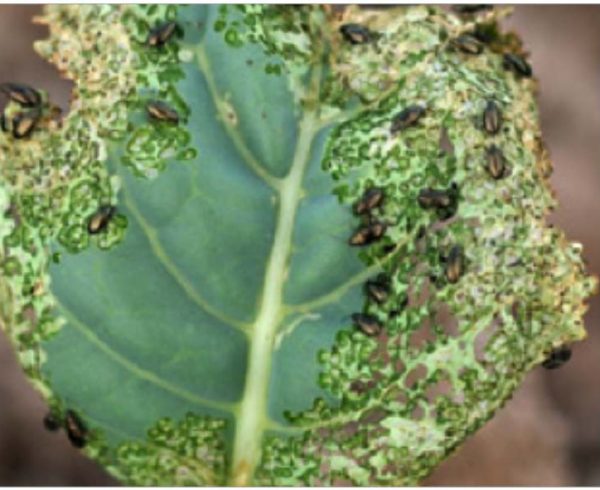 Flea beetle | Small insects that jump readily using muscles in their hind legs; hind legs appear swollen | Common in spring on seedlings; shot-hole feeding symptoms on small leaves |
|
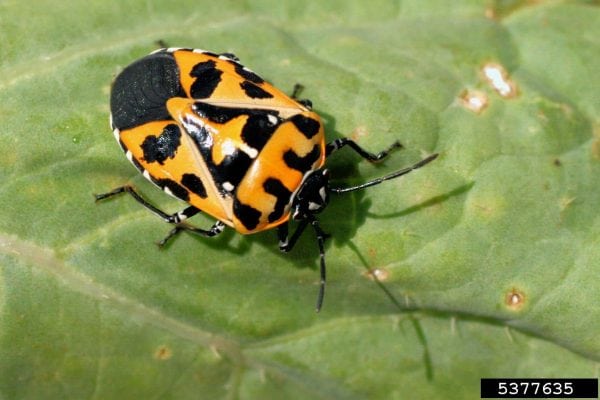 Harlequin bug | Brightly colored bugs with piercing-sucking mouthparts (orange, red, and yellow patterns on adults); eggs are barrel-shaped with black bands on top; overwinter as adults | Nymphs and adults feed on leaf veins causing extensive browning or wilting of leaves; extensive feeding will cause plants to wilt and die |
|
 Yellow-margined leaf beetle (YMLB) | Adult beetles are 5 mm long and dark brown with a yellow wing margin; eggs are bright orange, oval shaped, and laid in masses; caterpillars are dark brown with black head; body is covered with stout hair | Caterpillars feed together in mass during early instar and then scatter later; caterpillars cause extensive leaf feeding and crop damage occurs rapidly |
|
- IPM Scouting Sheets for Crucifer Crops
- Observation Sheet Example of Caterpillar Pests